Control Flow
Selenium IDE comes with commands that enable you to add conditional logic and looping to your tests.
This enables you to execute commands (or a set of commands) only when certain conditions in your application are met, or execute command(s) repeatedly based on pre-defined criteria.
JavaScript Expressions
Conditions in your application are checked by using JavaScript expressions.
You can use the execute script or execute async script commands to run a snippet of JavaScript at any point during your test and store the result in a variable. These variables can be used in a control flow command.
You can also use JavaScript expressions directly in the control flow commands.
Available Commands
Control Flow commands work by specifying opening and closing commands to denote a set (or block) of commands.
Here are each of the available control flow commands accompanied by their companion and/or closing commands.
if,else if,else,endtimes,enddo,repeat ifwhile,end
Let's step through examples of each.
Conditional Branching
Conditional branching enables you to change the behavior in your test.
if
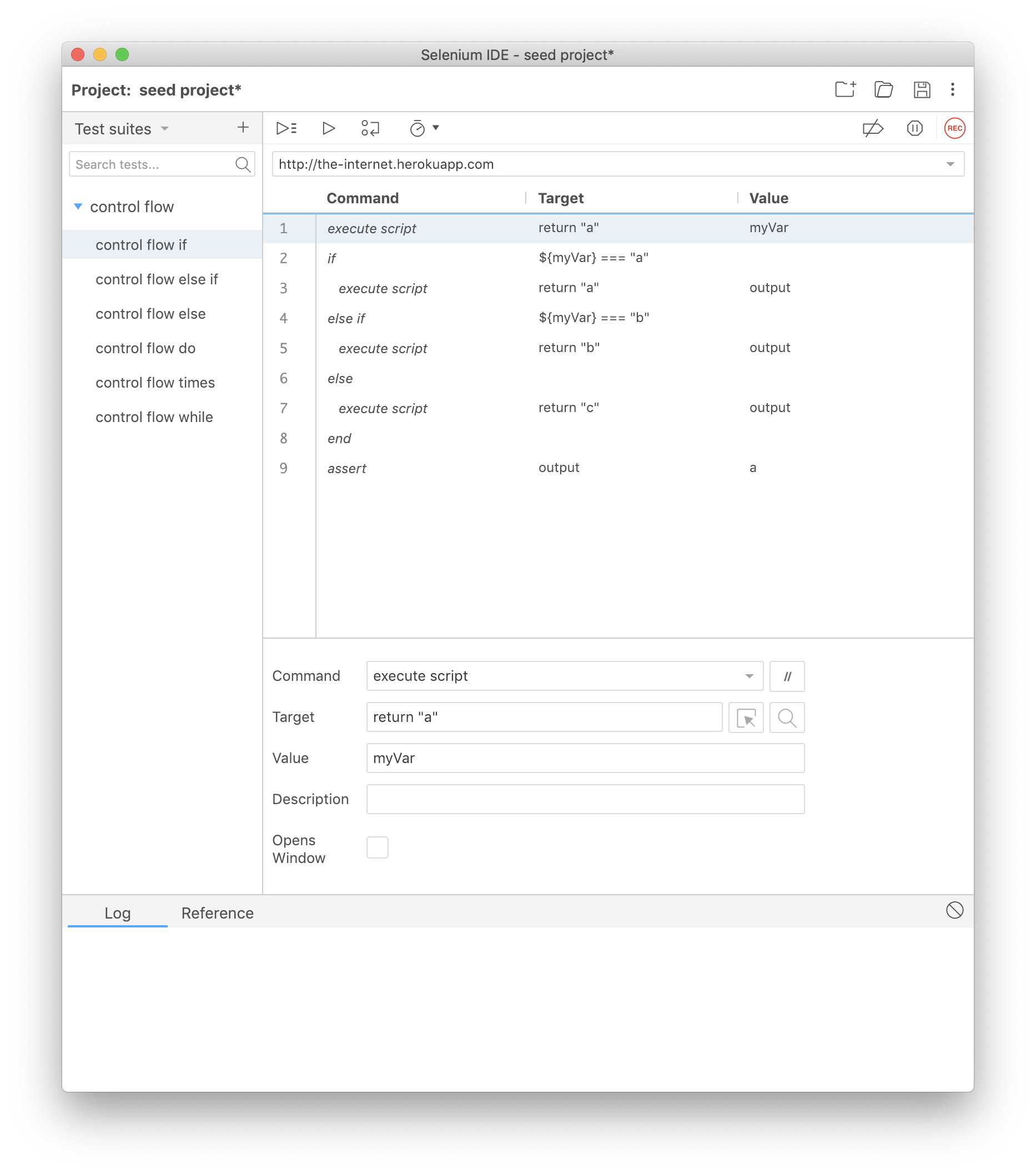
This is the opening command for a conditional block.
Along with it you provide a JavaScript expression you would like to evaluate. This can consist of variables created from prior JavaScript expressions in your test. This all goes in the target input field of the if command.
If the expression evaluates to true then the test will execute the commands that follow it up until the next conditional control flow command (e.g., else if, else, or end).
If the expression evaluates to false it will skip the commands that follow and jump to the next relevant conditional control flow command (e.g., else if, else, or end).
else if
This command is used within an if command block.
Just like with if it takes a JavaScript expression in the target input field to evaluate, executing either the command branch that follows it, or skips to the next relevant control flow command (e.g., else or end).
else
else is the final condition you can have in an if block. When none of the prior conditions are met, this command branch will be executed.
After it's done it will jump to the end command.
end
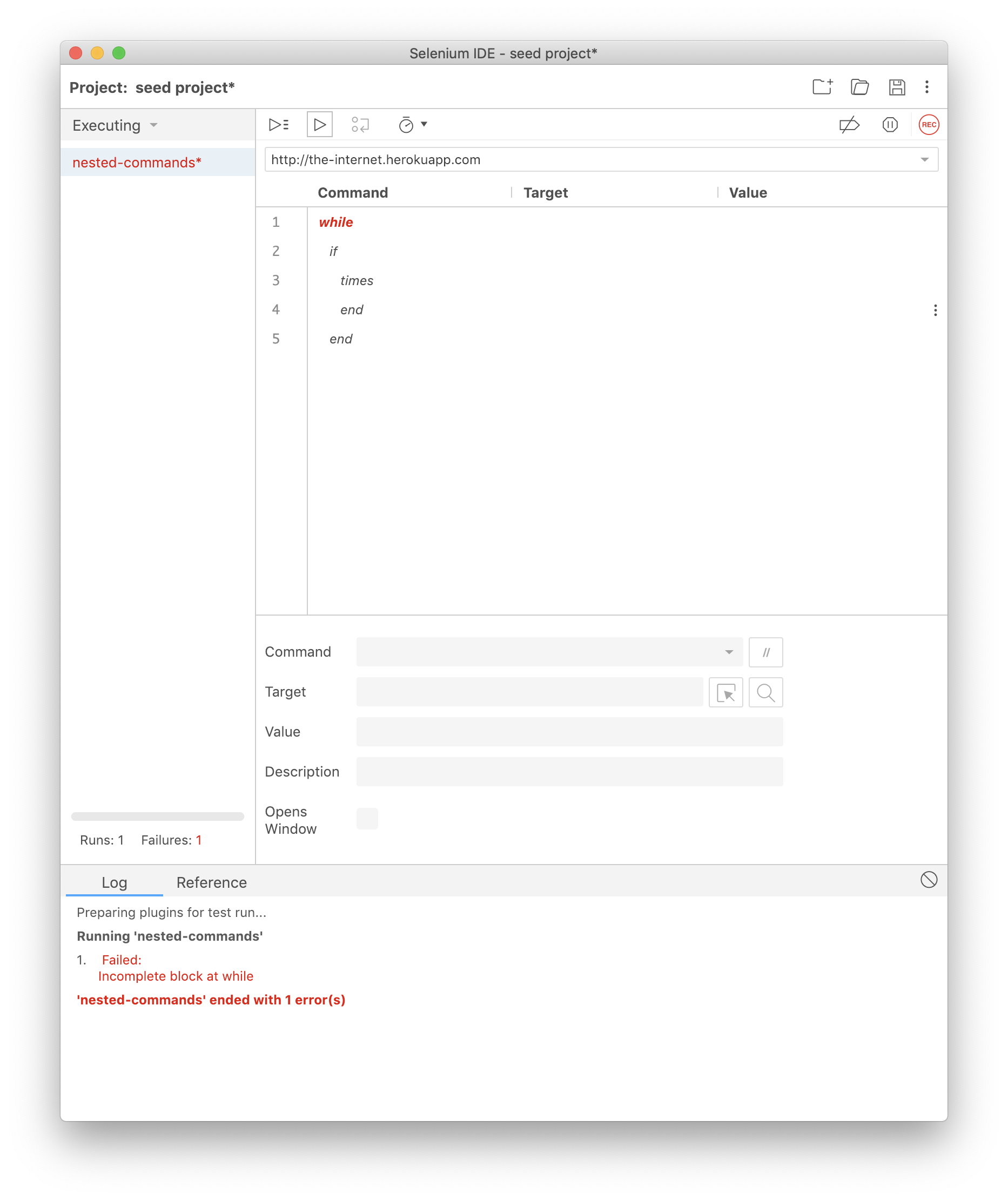
This command terminates the conditional command block. Without it the command block is incomplete and you'll receive a helpful error message letting you know when trying to run your test.
Looping
Looping enables you to iterate over a given set of commands.
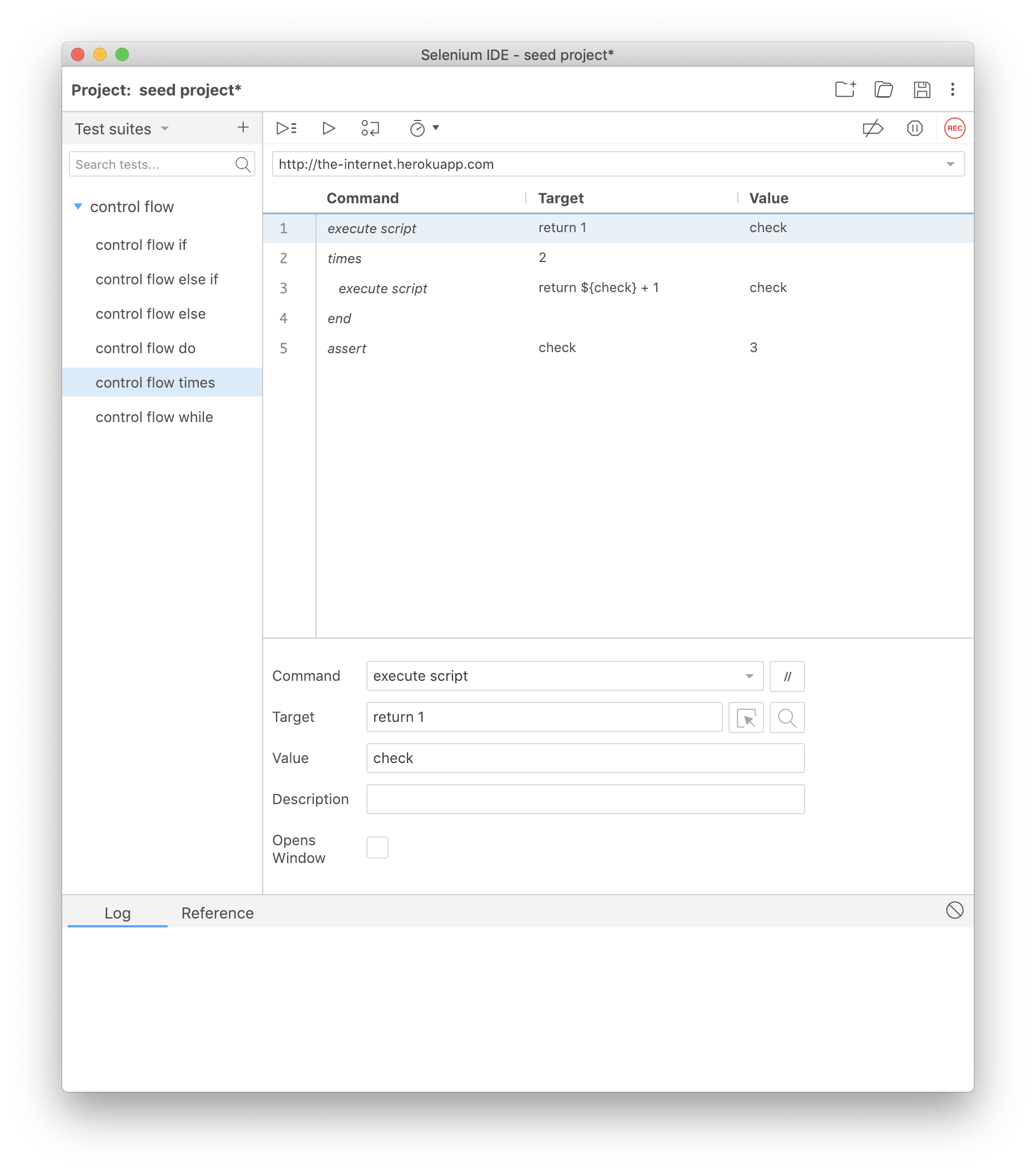
times
With times you can specify a number of iterations you would like to perform a set of commands. The number goes into the target input field of the times command.
To close the times command block be sure to use the end command.
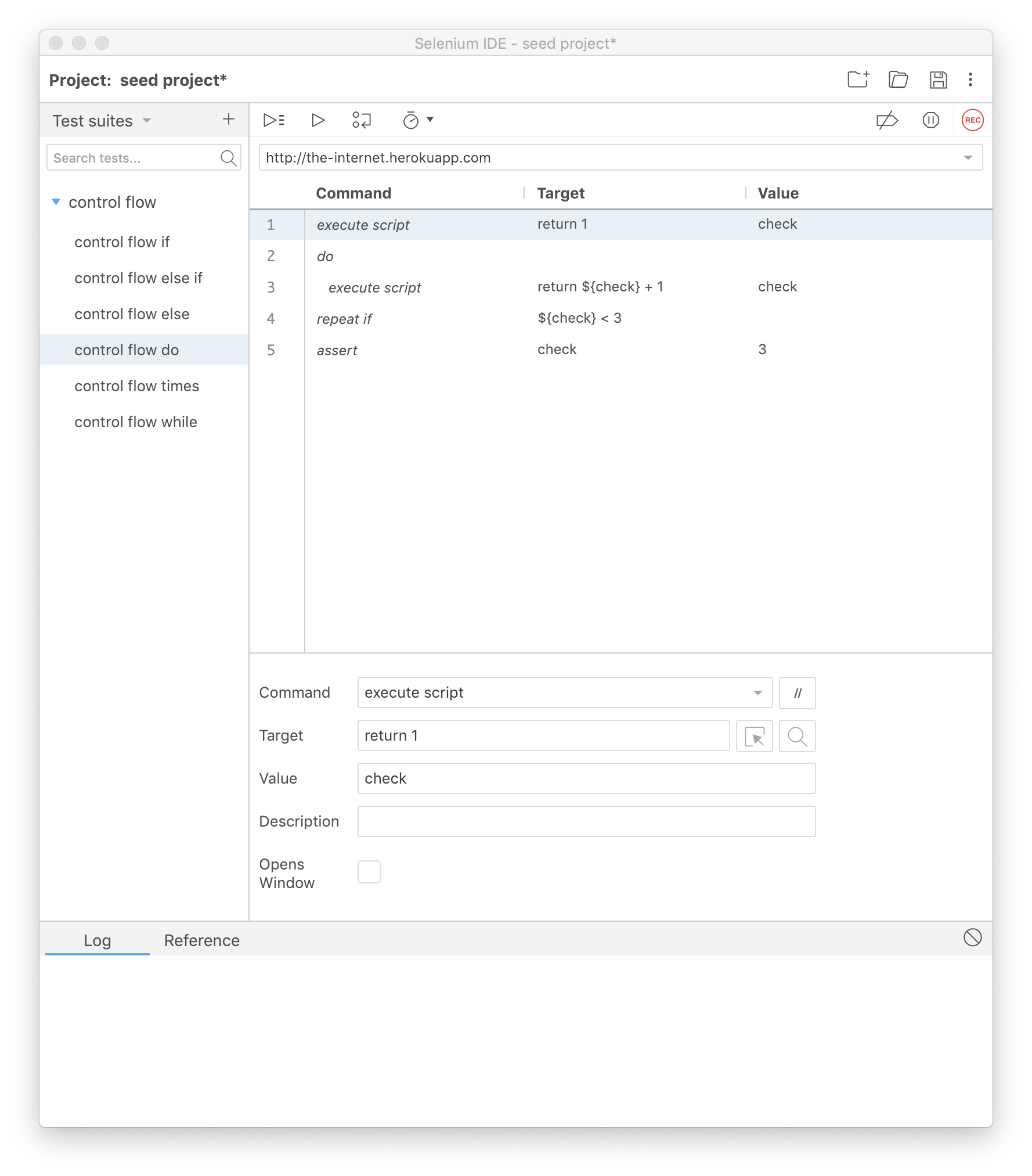
do
You start this loop with the do command, followed by the command(s) that you want executed, and end with the repeat if command. repeat if takes a JavaScript expression you would like to evaluate in the target input field.
The commands after the do will be executed first and then the expression in the repeat if will be evaluated. If the expression returns true then the test will jump back to the do command and repeat the sequence.
This will continue until either the condition returns false or the infinite loop protection is triggered -- which defaults to 1000 attempts. You can override this default by specifying a number in the value input field of the repeat if command.
while
With while you provide a JavaScript expression you would like to evaluate in the target input field. If it evaluates to true the command block that follows will execute until it reaches the end command.
Once done the test will jump back to the while command and repeat the same sequence over (checking first to see if the condition evalautes to true or false).
To close the while command block use the end command.
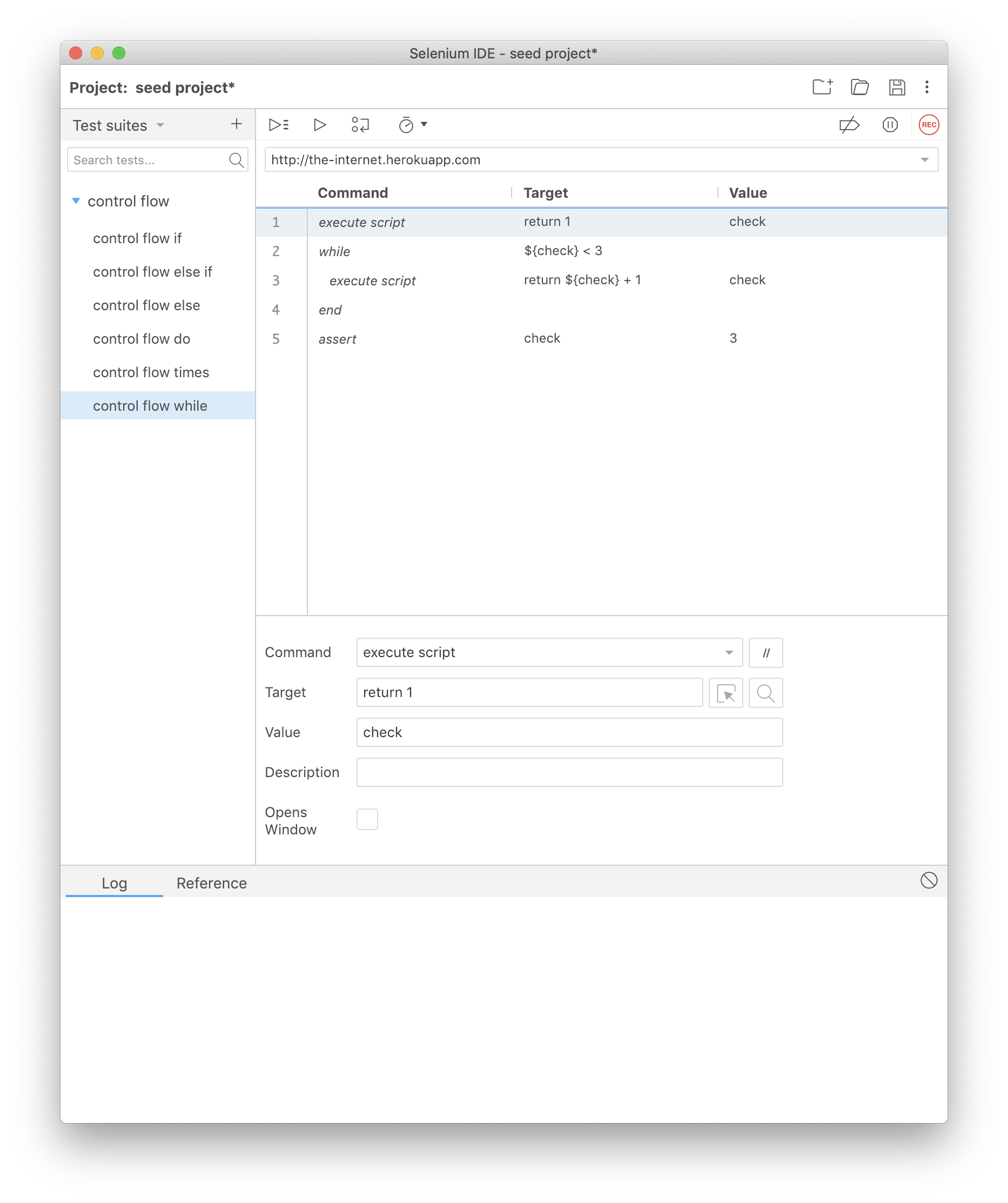
The loop will retry until either the condition returns false or the infinite loop protection is triggered -- which defaults to 1000 attempts. You can override this default by specifying a number in the value input field of the while command.
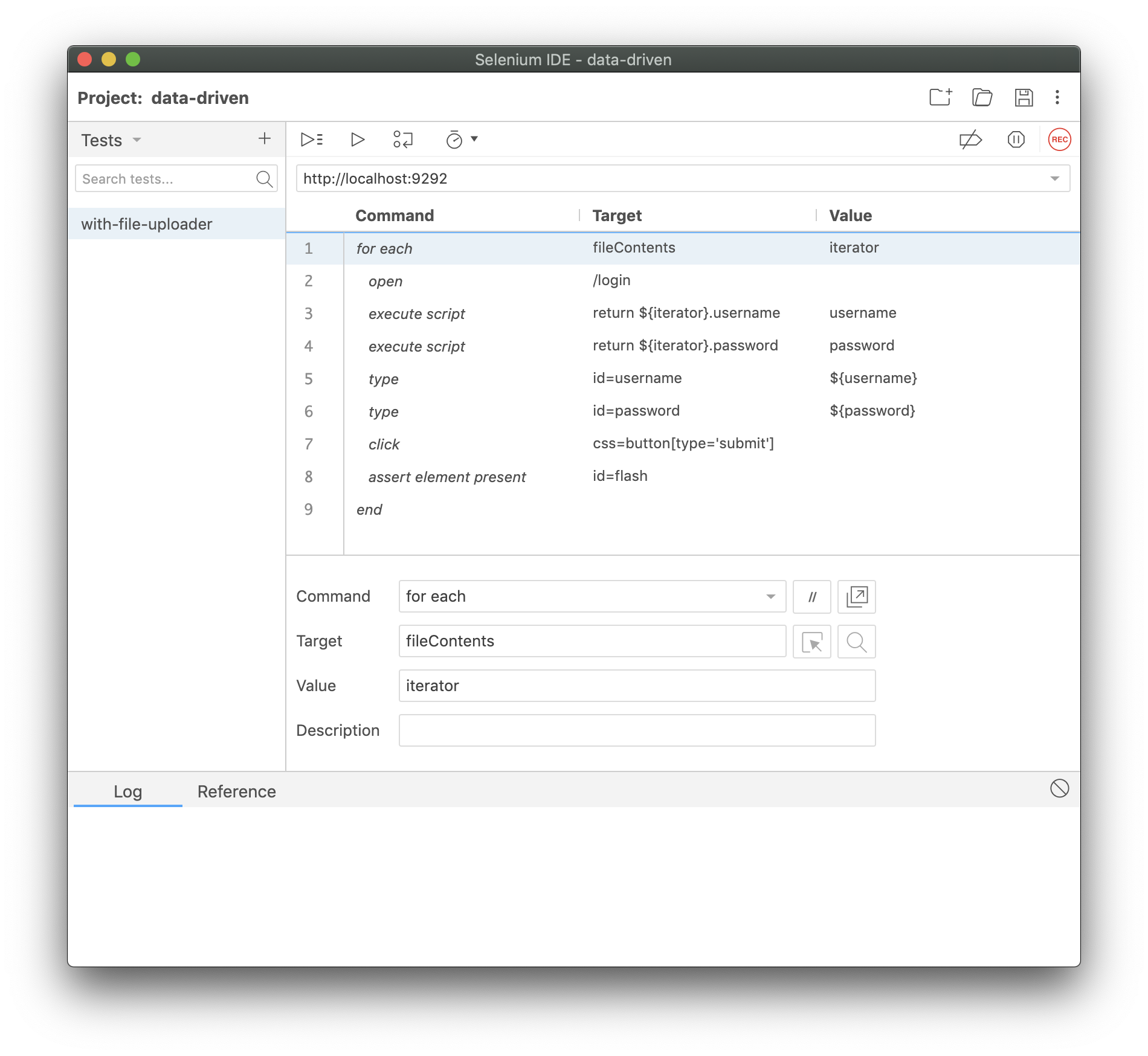
forEach
Saving the best for last, we have the ability to iterate over a collection (e.g., a JS array) and reference each item in that collection while we do it.
In the target field you specify the name of the variable that contains the array you want to iterate over. In the value field you specify the name for the iterator variable you'd like to use. For each entry in the array, the commands that follow will be executed. During each iteration the contents of the current entry will be accessible through the iterator variable.
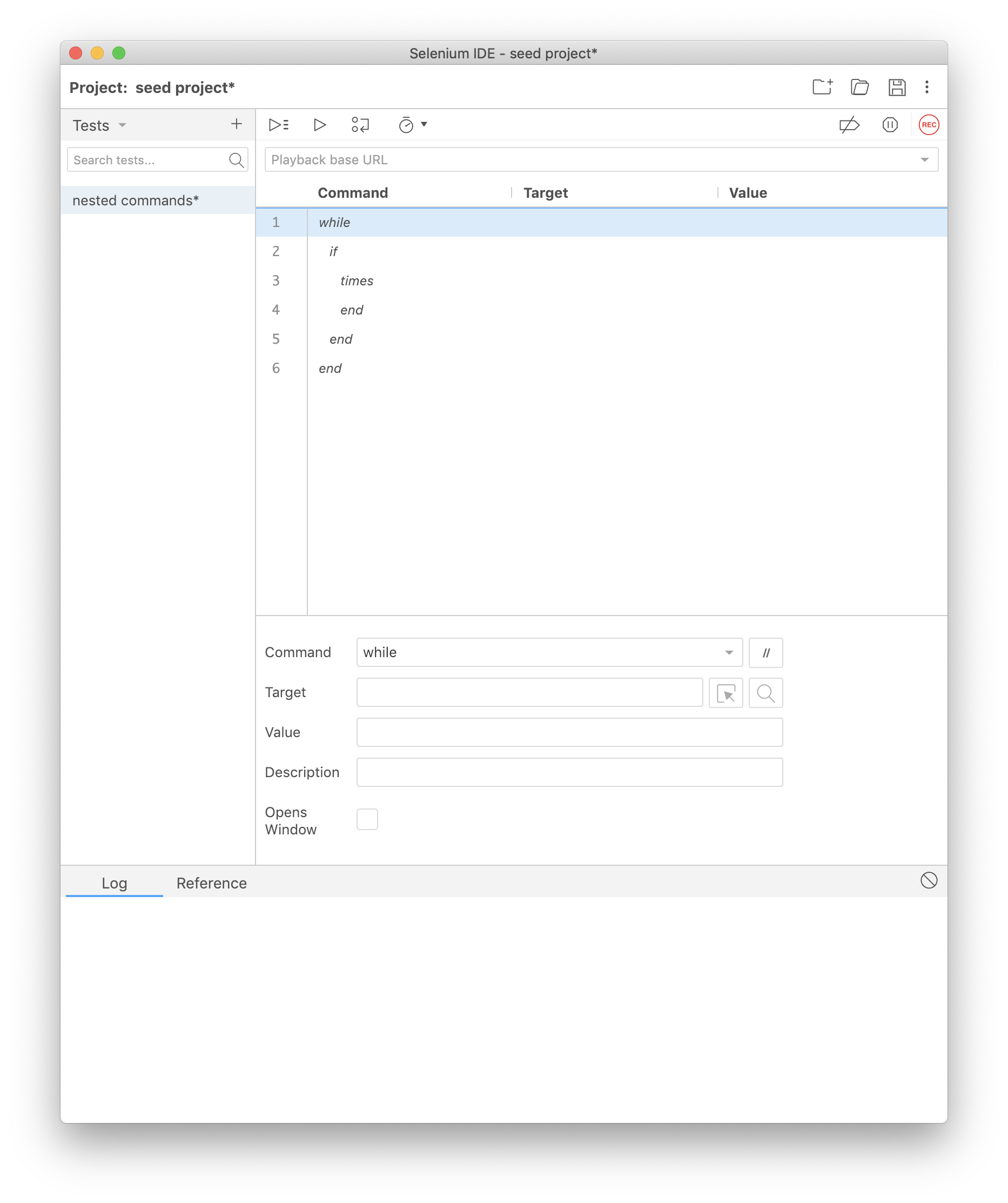
Nesting Commands
You can nest control flow commands as necessary (e.g., an if block can go inside of a while block, and vice versa).
Syntax Validation
If you're not sure if your control flow syntax is correct try running your test to see. The IDE will spot errors in the control flow syntax and call out the specific command that is incorrect or missing.